Developments in the field of medical robots are extremely fast. The breakneck speed leads to malicious gossip about surgeons no longer being needed and robots taking over the operating theatres, but such anxiety is uncalled for. Surgeons will always have a dominating presence in operating theatres, but they will more and more often be assisted by smart, ultra-small medical robots. This article will present a number of medical developments across the world.
The worldwide market of medical robotics will continue to grow. In 2017 the market size was only €5 billion, but by 2023 it is expected to have risen by 300% and the end of this trend is not in sight.
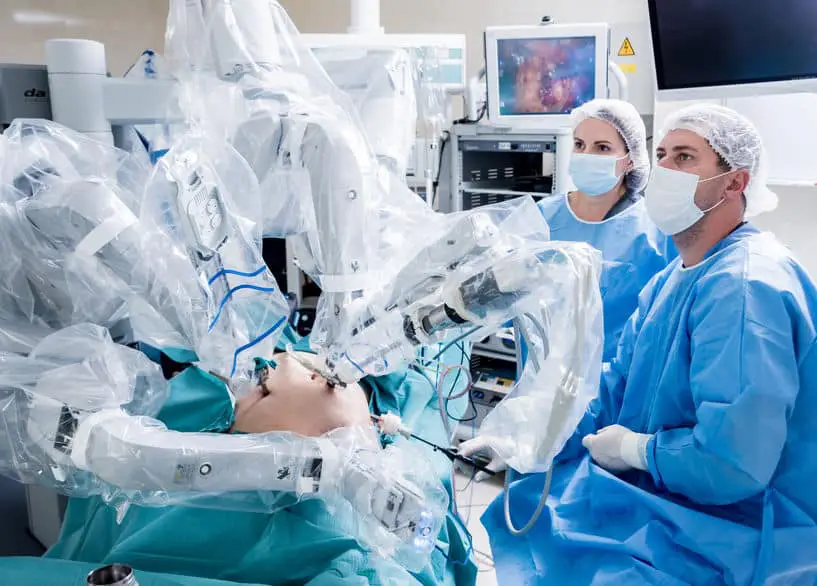
Medical robots are currently deployed in minimally invasive surgery. This makes that type of surgery less risky for the patient, fewer cuts are required, it is less painful and recovery will be faster. The system used for this is the Da Vinci system, and it has been used in over six million operations all across the world. The system is not flawless at the moment, though, but it is still safer and more adequate than traditional surgery.
Sensor technology is frequently used to effectively deploy medical robots. Add to this artificial intelligence, and you have a winning combination. It allows medical robots to be absolutely tiny and extremely advanced. There is, for example, a robot catheter that can autonomously find its way through a patient’s body. The built-in sensor is an optical touch sensor. On the basis of what it feels it can determine what part of the body it touches, whether it be the heart’s walls, a heart valve or a blood vessel. The programmed algorithms make it find its way in the human body and manoeuvre itself into the right position.
A team of MIT employees has developed a magnetically controlled robotic thread. This thread is so minute that it can work its way through brain vessels. This allows it to treat blockages and lesions, such as those that occur in aneurysms and strokes.
These days virtual reality is also a staple in operating theatres. When linked to a medical robot it can not only allow a surgeon to see inside a person’s body, but also e.g. abdominal operations can be done by a miniature robot present in the abdomen which mimics one-on-one the surgery that the surgeon performs in the operating theatre.
Medical robots will be a wonderful addition to the medical world. The use of robots will enable us to help patients without the need to have a specialist present in the room. People in places that are difficult to access can also be treated. The need for medical experts remains undisputed, also in the future, but their operational role will change.